In today's digital landscape, cybersecurity frameworks are essential for organisations to protect their data, systems, and critical assets from evolving threats. Risk management and adherence are two vital elements for these frameworks to be effective. While these concepts may seem simple, they are the backbone of a successful cybersecurity strategy. Without them, even the most carefully designed frameworks can fail.
We surveyed to assess the overall sentiment on the most vital component of any framework within cybersecurity.
The options provided were as follows:
- Risk management
- Threats and vulnerabilities
- Adherence
- Efficient use of resources
After collecting survey responses, we carefully analysed the data and provided a detailed analysis for each option. Additionally, we explained the significance of each selection and presented opposing viewpoints to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the topic. These survey findings provide valuable insights into the views and priorities of cybersecurity professionals, which can inform our discussions on the importance of compliance and responsibility in cybersecurity frameworks.
We want to express our gratitude to everyone participating in the poll.
Thank you for your valuable participation!
The cornerstone of any framework is adherence.
Regardless of a framework's design or comprehensiveness, its validity hinges on its consistent respect, observance, and application. Adherence guarantees the accurate and effective implementation of the framework's principles, controls, and processes.
This is connected to responsibility, which we underscored in our earlier conversation. Discover more insights in this compelling article: "Who needs frameworks anyway?"
Everyone involved must be accountable for meeting the framework's guidelines. Without adherence and a sense of accountability, even the most robust frameworks lose their value, becoming theoretical documents without real-world impact.
Uncover the latest insights on why risk management is the cornerstone of effective cybersecurity
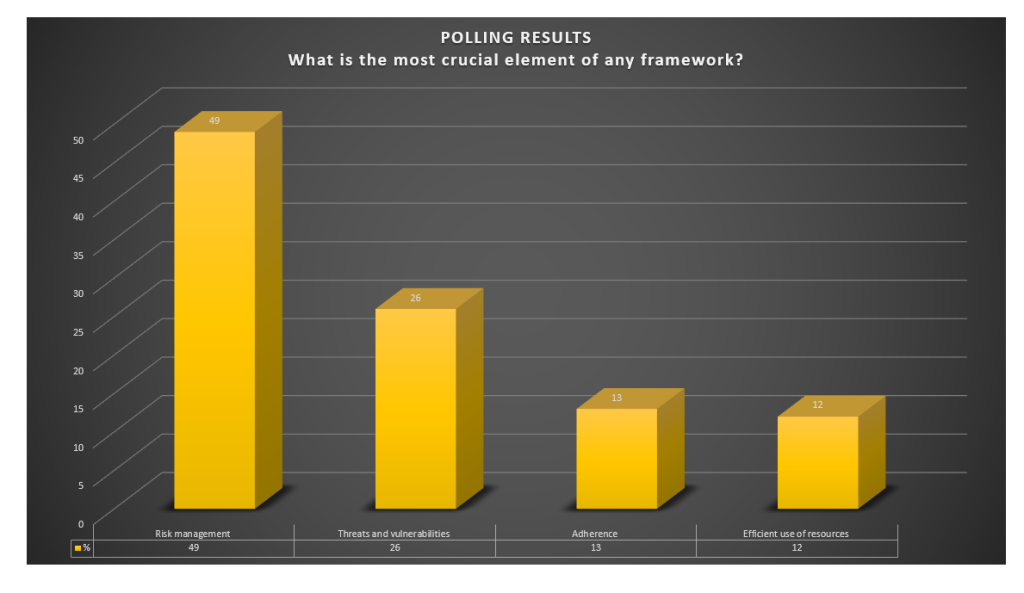
In a recent survey, 49% of participants highlighted risk management as the most crucial element of any cybersecurity framework. This underscores the widely shared belief that effectively handling risks is essential for safeguarding an organisation's assets. Let's delve into why this perspective is prevalent and consider counterarguments from other viewpoints.

Why Risk Management is Seen as the Most Crucial Component
Focus on Prioritisation
Risk management helps organisations identify and prioritise their most significant threats and vulnerabilities, allowing them to allocate resources effectively. Without this focus, companies may spend time and effort on less impactful security measures, leaving them exposed to critical risks.
Dynamic and Evolving Threat Landscape
The cybersecurity threat landscape is constantly changing. Risk management offers a flexible, adaptable approach for organisations to update their defences in response to new vulnerabilities or evolving business environments.
Resource Allocation
Risk management guides decision-making, ensuring organisations invest in the right tools, technologies, and processes to mitigate high-priority risks while avoiding unnecessary expenses. This efficiency is crucial in environments with constrained budgets.

Contact us now to elevate your security with remote SOC management!
Alignment with Business Goals
Effective risk management ensures cybersecurity initiatives align with broader business objectives, minimising disruptions while safeguarding critical assets. This balance between security and operational continuity helps organisations navigate the trade-offs between security and functionality.
The Counterargument
Why Risk Management Alone Isn't Sufficient.
While risk management is crucial, some argue it's just one aspect of the cybersecurity puzzle.
Below are counterarguments emphasising the importance of other components:
Adherence is crucial
A sound risk management strategy can only succeed if employees follow established controls, policies, and guidelines. Organisations need the consistent application of security measures to be protected.
Threats and Vulnerabilities Are Fundamental
A focus on threats and vulnerabilities directly helps organisations address specific weaknesses. Threat intelligence and vulnerability assessments allow security teams to take proactive measures, reducing risks before they escalate into serious incidents.
Ensure efficient use of resources
Ensuring efficient resource use is crucial in budget-constrained environments. Organisations must maximise security investments for cost-effective, sustainable risk management.
A comprehensive approach is essential in cybersecurity frameworks. This necessitates integrating risk management with other crucial elements such as compliance, efficient resource utilisation, and vulnerability mitigation. Organisations may disproportionately emphasise one area without this comprehensive perspective while neglecting other equally critical components.
The survey results show that 49% prioritise risk management, highlighting its significance in today's cybersecurity landscape. However, a robust cybersecurity framework requires balancing risk management, adherence, vulnerability mitigation, and resource efficiency.

The Importance of Addressing Threats and Vulnerabilities in Cybersecurity
In the same survey, 26% of respondents selected threats and vulnerabilities as the most crucial component of a cybersecurity framework. Let's delve into the reasons behind this viewpoint and consider counterarguments from alternative perspectives.
Why Threats and Vulnerabilities Are Considered Essential for Proactive Defense
Focusing on threats and vulnerabilities enables a proactive approach, addressing weaknesses before they are exploited. This approach prevents attacks rather than simply mitigating their impact after the fact.
Strategic Precision:
Directing attention to vulnerabilities offers a clear framework for security operations. This approach ensures that we take specific, practical actions to fix identified weaknesses, such as addressing known vulnerabilities through patching or implementing targeted firewall rules.
Current Security Posture:
Given the evolving nature of cyber threats and the continual discovery of new vulnerabilities, prioritising threats and vulnerabilities ensures organisational agility, enabling the maintenance of current preparedness to counter emerging risks.
Clear Indicators for Action:
Focusing on threats and vulnerabilities provides organisations with measurable data upon which to act. This helps justify decisions to leadership, making it easier to explain why specific security steps are necessary.
The Counterargument
Why Threats and Vulnerabilities Alone May Not Be Enough
While focusing on vulnerabilities is critical, it doesn't offer the complete picture.
Here's why:
Risk Context is Missing:
Without risk management, focusing too much on vulnerabilities can lead to misaligned priorities. Not all vulnerabilities pose the same level of risk, and some threats may not be relevant. Risk management ensures resources are allocated to the most pressing issues.
Reactive vs. Strategic:
Emphasising vulnerabilities alone can lead to a reactive security strategy, with organisations continuously firefighting instead of establishing long-term, proactive defences.
Adherence and Accountability:
Although identified and accompanied by an available patch, a vulnerability may remain unaddressed in the absence of adherence to established security policies. Adherence to these policies is imperative to implement robust security measures consistently.
Resource Drain:
Focusing solely on vulnerabilities can overwhelm security teams, draining resources. This may lead to burnout and an inability to address more critical risks.
The 26% of respondents prioritising threats and vulnerabilities demonstrate the significance of identifying and addressing potential risks early on. However, it's important for organisations not to become too focused on less critical vulnerabilities and overlook more significant, more strategic risks within the broader context of risk management and compliance.

Adherence: An Underappreciated Element of Cybersecurity
13% of the survey respondents chose adherence as the most crucial element of a cybersecurity framework. Let's delve into why this is often underestimated and why adherence is essential.
Why Adherence Is Crucial
Consistency in Implementation:
Adherence ensures that established security measures and policies are consistently followed. Without proper implementation, even the best-designed cybersecurity framework will fail.
Reduces Human Error:
Human error remains a major cause of security breaches. By promoting strict adherence to protocols, such as patch management and access controls, organisations can minimise risks caused by employee mistakes.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements:
Many industries have strict compliance regulations, such as GDPR and PCI-DSS. Adherence ensures organisations remain compliant with these requirements, avoiding legal consequences and reputational damage.
Enables Accountability:
Adherence cultivates a culture of accountability, ensuring that all organisational members take cybersecurity seriously and consistently adhere to established controls.
The survey results for adherence were relatively low for several reasons
Perception of Being Secondary:
Adherence may be seen as a supporting function, with respondents feeling active roles such as risk management or vulnerability management are more critical.
Focus on Technical Solutions:
Cybersecurity conversations often focus on technical solutions, such as firewalls or encryption, rather than compliance and policy adherence.
Adherence may be overlooked, but ensuring that security measures are regularly and efficiently implemented is critical. Other security initiatives may only succeed if adherence is maintained, making it an essential but frequently ignored component of any cybersecurity strategy.

Efficient Use of Resources: The Practical Side of Cybersecurity
Although only 12% of respondents identified the efficient use of resources as the most vital component, this perspective highlights the practical realities many organisations face.
Efficient Resource Utilisation and Maximising Security within Limited Budgets
Financial constraints are prevalent in many organisations, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Therefore, it is imperative to ensure that each investment in cybersecurity yields optimal protection.
Prioritising Based on Risk:
Efficient resource use involves allocating resources to areas with the highest risks, ensuring that critical assets are protected first.
Human Resources and Skills:
Resource efficiency includes making the best use of available human capital, especially considering the global shortage of cybersecurity professionals.
The survey indicates that efficient resource use may represent the smallest group, yet it underscores the necessity for practical and scalable security strategies, particularly in budget-constrained environments.
The survey emphasises a wide range of perspectives on the most crucial component of any cybersecurity framework. While risk management is frequently mentioned, addressing threats, vulnerabilities, adherence, and efficient resource use should not be underestimated. A balanced approach that integrates all these components will establish any organisation's most robust cybersecurity framework.
Embracing Risk Management: The Key Element of Every Cybersecurity Framework
Within any cybersecurity-related framework, risk management serves as the cornerstone. Cybersecurity inherently revolves around the adept management of risks. Each organisation encounters a spectrum of threats, encompassing internal vulnerabilities and external attacks. Hence, the paramount objective of a cybersecurity framework is to facilitate the productive identification, assessment, and mitigation of these risks.
Risk Management
Risk management ensures that organisations:
- Identify any threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise an organisation's systems or data.
- Understand the probability and potential impact of each risk to prioritise efforts.
- Implement specific controls and measures customised to mitigate the highest risks.
The primary objective is to optimise resource allocation by concentrating on the most critical areas. This ensures that the organisation protects its assets effectively without expending resources on low-priority threats. A framework's effectiveness depends on its ability to reduce risk.
It's important to note that risk management is an ongoing process, not a one-time task.

As threats evolve, the approach to addressing them must also evolve. This is why frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), ISO/IEC 27001, and the Australian Information Security Manual (ISM) emphasise regular risk assessments and adaptable control measures.
Adherence

Adherence: The Operational Backbone
- a powerful phrase that encapsulates the essential role of adherence in ensuring smooth operational processes.
Risk management is crucial, but adherence is the operational foundation of any cybersecurity framework. A well-designed framework with strong risk management is only effective if consistently followed across the organisation. Adherence ensures that every security control, process, and policy outlined in the framework is implemented, monitored, and maintained correctly.
Adhering to security best practices offers several key benefits:
- Consistency in security practices ensures that every department follows the same standards.
- Regulatory compliance involves aligning with mandated requirements such as GDPR, PCI-DSS, or the ISO 27001 framework.
- Reduced human error is achieved by strictly adhering to security policies and protocols, addressing a common weak point in cybersecurity.
Organisations must nurture a culture of security awareness and accountability to ensure successful adherence. Training employees and ensuring they comprehend the significance of adhering to security protocols to prevent breaches resulting from negligence or misconfigurations is essential.
Even a flawlessly executed risk management strategy can only succeed with adherence.
While risks may be identified and controls recommended, their practical implementation depends on strict adherence to security protocols. Without consistent adherence, the organisation remains vulnerable to cyber threats despite controls.
Accountability
Ensuring Accountability: Driving Adherence and Risk Management
In cybersecurity, accountability plays a pivotal role in ensuring the meticulous execution of risk management and compliance measures. It is imperative that every individual, from the executive echelons to the system administrators, upholds responsibility for the preservation of cybersecurity controls.
Accountability is essential because it ensures that:
- The framework establishes clear expectations for each person's role in adhering to it.
- Consequences for failing to follow security guidelines are enforced to minimise the risk of negligent behaviour.
- Audits and feedback loops are used to assess adherence and continuously improve the framework.
Compliance can deteriorate rapidly without accountability, resulting in security gaps and rendering even the most robust risk management strategies ineffective. Therefore, organisations must establish explicit accountability structures to ensure that all individuals are accountable for adhering to the framework.
Exploring the Dynamic Relationship Between Risk Management and Adherence

In any cybersecurity framework, risk management and adherence are inseparable. Risk management helps identify threats, vulnerabilities, and necessary controls to protect an organisation. Adherence ensures that these controls are effectively applied. Together, they form a strong defence against cyber threats.
The cybersecurity framework's effectiveness hinges on a balanced approach, with equal emphasis on both risk management and adherence. Prioritising risk management without corresponding adherence can result in unexecuted or inadequately implemented controls. Conversely, adherence without proper risk management can lead to resource wastage on ineffective or unnecessary measures.

